
Limit/Position vs Safety Interlock vs Coded Magnetic Switches
Posted by Morgan Spano on Apr 4th 2022
The term “switch” can have many connotations in our industry.
The actual type of switch you happen to be dealing with breaks down into how the switch functions and its construction. We wanted to clarify the differences between Limit/Position Switches, Safety Interlock Key Switches and Non-Contact Coded Magnetic Switches.
Let’s start off with the basic functionality of our most common types of switches:
Designed to monitor and indicate the movement of an object by physically triggering the switch’s actuator. As the actuator is tripped, an electrical connection is either made or broken depending on how the application has been designed.
Types of Actuators:
- Roller Levers
- Rounded Plungers
- Roller Plungers
- Rod Lever
- Lateral Rounded Plunger
- Flexible Rod
- Cable Pull
- Rotative Axis
- Latch/Reset
Position/Limit Switch Applications:
- Aggregates and Mining
- Pharmaceutical and Chemical
- Paper, Pulp and Wood
- Steel, Aluminum and Precious Metal
- Automotive and Electronics
- Water and Recycling

Position/Limit Switch Advantages:
- Super versatile! Can be used in almost any industrial environment
- Precise accuracy and repeatability
- Low amounts of energy consumption
- High inductance load switching capability
- Can control multiple loads

Safety Interlock Keyed Switches
Focused on safety, these switches are enabled through a predetermined sequence of operations. Once engaged, the device cannot be released without the correct process. Generally these are installed on valves, gates, and entry ways to potentially dangerous environments.
Required Features:
- The lock can only be operated by the dedicated key – meaning you can’t cheat the lock by using something like a screwdriver
- It’s not possible to force the switch once engaged. Try to force the switch open and you’re likely to just break the key.
Safety Interlock Applications:
- Automotive and machine tool
- Complex and special machines
- Crane and hoist
- Food and beverage
- Packaging
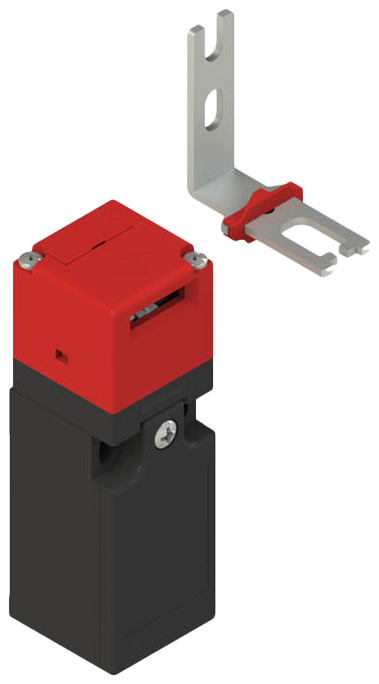
Safety Interlock Key Switch Advantages:
- Locking feature ensures both mechanical and personal safety
- Multiple actuator types to fit a wide variety of application requirements
- Generally rugged enclosures for demanding applications
- Small enclosure styles for mounting in tight spaces
- New versions can use RFID to monitor who has access and historical data
Safety Interlock Key Switch Disadvantages:
- Component wear and tear is inevitable
- Possible need for safety circuit for proper operation resulting in higher project costs
- If the switch needs to be repaired or completely breaks, the machine will be down until repairs are completed

Non-Contact Coded Magnetic Switches (CMS)
Non-contact coded magnetic switches work by pairing a magnetically-actuated reed contact and specially-coded actuator. In most applications an interlock is a device used to help prevent a machine from harming its operator or damaging itself by stopping the machine when tripped.
Non-contact safety switches are ideal in applications where precise guidance of guards is difficult. Due to their design, they are extremely long-lasting devices that require minimal maintenance. In addition, they are resistant to shock and vibrations and offer a high level of prevention against tampering.

Ideal for sliding, hinge, or lift-off machine guard doors, non-contact switches offer simple setup and alignment, less wear, and fully-sealed IP67 and IP69K housings.
Applications Criteria:
- When poor guard alignment exists
- Anti-tamper sensing is required
- High hygiene requirements exist, e.g. food industry hose down
- Long life requirement (no moving or touching parts)
- LED status indication is desirable

Coded Magnetic Switches Advantages:
- Can be mounted under non-magnetic materials
- Short stopping times for demanding applications
- Flexible alignment options compared to switches that require perfect alignment
- Highly tamperproof
- Longer lifespan
- Low maintenance cost/requirements
- A variety of designs allow for use in many types of applications
Coded Magnetic Switches Disadvantages:
- Because of the actual range needed to make or break the circuit, the machine may run even if the door or entry is not 100% closed
- For some models, if one side breaks, the entire switch may need to be replaced
